Gartner predicts disaster recovery will become part of the CISO’s job. This isn’t just an IT problem anymore—it’s an enterprise imperative.
Leveraging Cyber Threat Intelligence to Empower SOC Teams


Executive summary
Security Operations Centers (SOCs) are overwhelmed by alerts, often reacting to threats as they appear rather than anticipating them. Bitsight Threat Intelligence (TI) transforms SOC operations by providing external visibility, context, and correlation with real adversary behavior. By mapping incidents to MITRE ATT&CK techniques and monitoring the deep and dark web for emerging risks, Bitsight TI enables SOC and CTI teams to detect, understand, and prevent threats before they cause impact.
The role of the SOC in modern cyber defense
SOCs sit at the heart of every organization’s cyber defense strategy, continuously monitoring, detecting, and responding to threats. Today’s adversaries move faster than ever, using automation, supply chain weaknesses, and AI-driven tactics to stay ahead.
CTI changes that dynamic. By integrating CTI into SOC workflows, organizations shift from reactive defense to proactive, intelligence-driven operations. At Bitsight, we see how actionable intelligence helps SOC teams anticipate risk, prioritize critical alerts, and improve response outcomes.
The reality of SOC operations: Fast, reactive, and high volume
Modern SOCs handle thousands of alerts every day. Analysts must triage and contain threats quickly, often with limited context. Their focus is on identifying abnormalities and restoring normal operations, not necessarily on attribution or campaign analysis.
SOCs encounter a constant mix of real threats and false positives. For example, a user who accidentally mistypes their password three times might trigger a brute-force detection rule, creating an alert that looks suspicious but is actually harmless. These mundane alerts can consume analyst time and obscure truly malicious activity.
Other anomalies are more serious indicators of compromise, such as:
- Time stomping (T1070.006): Attackers modify file timestamps to hide malicious activity
- Brute force (T1110): Automated login attempts targeting weak credentials
- Dictionary password sprays (T1110.001): Broad, low-and-slow attempts using common passwords
- PowerShell misuse (T1059.001): Encoded or obfuscated scripts for persistence or lateral movement
Without the right intelligence, it’s difficult for SOC analysts to distinguish benign behavior from real adversary activity. Bitsight TI provides that context by translating raw indicators of compromise (IOCs) into known tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) aligned with MITRE ATT&CK T-codes and associated threat actors. This clarity allows SOC teams to focus on genuine threats and reduce time wasted on false positives.
How threat intelligence teams expand the picture
While SOCs fight daily fires, threat intelligence teams dig deeper to understand the broader threat landscape and adversarial intent.
1. Deep and dark web reconnaissance
Bitsight TI monitors underground marketplaces, encrypted forums, and threat actor channels for early indicators of targeting activity. Mentions of company domains, credentials for sale, or stolen data provide early warning that allows SOCs to act before an attack occurs.
Example: Detecting RDP or VPN credentials listed for sale (T1078 – Valid Accounts) can prompt SOCs to harden access controls immediately.
2. Tracking threat actor infrastructure and behavior
Bitsight continuously observes malicious domains, IPs, and artifacts to map threat actor infrastructure. By aligning this data to the MITRE ATT&CK framework, Bitsight identifies how attackers operate across the kill chain, from initial access (T1190) to data exfiltration (T1041), providing SOCs with intelligence they can operationalize.
3. Predictive threat targeting analysis
Bitsight TI correlates attack data across industries to predict which adversaries are most likely to target a specific organization or sector. If credential spraying (T1110.003) and phishing (T1566.001) activity increases among a known ransomware group, Bitsight can alert similar organizations to prepare and prevent impact.
4. Translating SOC activity into intelligence
CTI analysts take SOC-generated telemetry, such as brute-force attempts, encoded scripts, and lateral movement, and translate it into structured intelligence mapped to TTPs and adversaries. This transforms raw alerts into actionable narratives that link activity to specific threat actors or campaigns.
Bitsight MITRE ATT&CK T-code tracking
Bitsight’s TI platform maps adversary behaviors directly to MITRE ATT&CK techniques and sub-techniques (T-codes). This structured approach gives SOC and CTI teams a shared language for detection, investigation, and response.
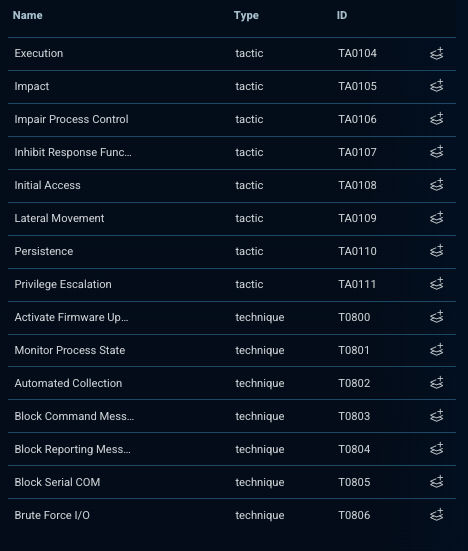
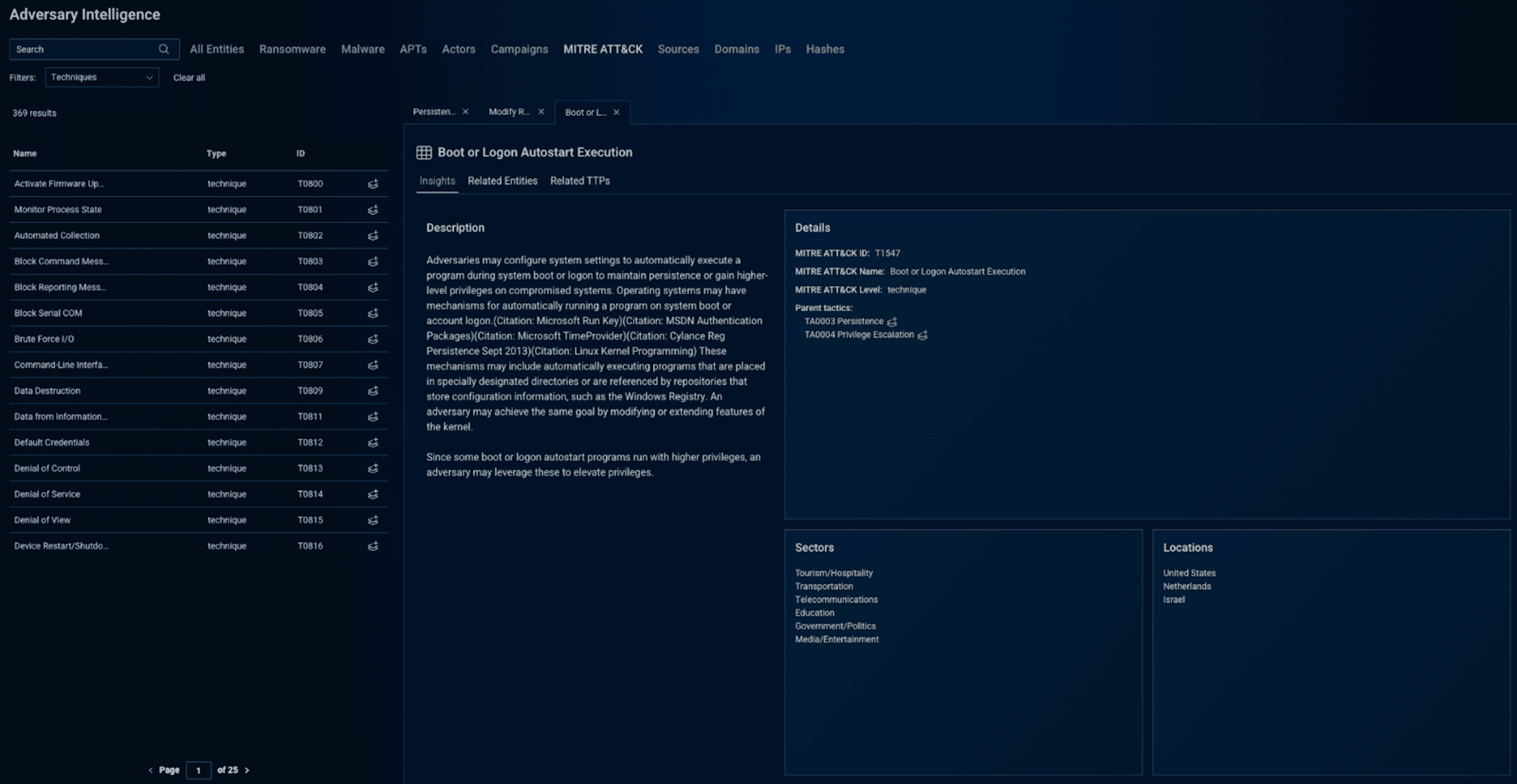
Bitsight’s T-code tracking provides:
- Behavioral mapping: Each IOC is tied to a T-code, such as
- Credential access – brute force (T1110)
- Defense evasion – time stomping (T1070.006)
- Execution – PowerShell (T1059.001)
- Persistence – scheduled task creation (T1053.005)
- Exfiltration – exfiltration over web service (T1567.002)
- Adversary alignment: Bitsight correlates T-codes to known threat actors for accurate attribution and campaign tracking
- Visual reporting: SOCs can see which techniques are being leveraged against them and how they relate to larger adversary behaviors
This alignment ensures that both SOC and CTI teams operate with consistent intelligence and faster, more precise response coordination.
How CTI supports SOC functions
CTI gives SOCs early warning and external visibility that traditional alert-based models lack.
- Anticipate threats: Bitsight identifies malicious infrastructure and campaigns targeting specific sectors
- Reduce alert fatigue: Enrichment helps analysts focus on meaningful alerts and filter out noise like benign user errors
- Accelerate investigations: Integrating CTI with SIEMs and SOARs automates correlation and enrichment for faster containment
Enhancing threat hunting and discovery
Bitsight TI strengthens proactive threat hunting by enabling analysts to look for undetected malicious activity.
- Proactive IOC searches based on active threat campaigns
- MITRE ATT&CK alignment to identify adversaries using shared TTPs
- Continuous intelligence updates that refine detection logic and reduce dwell time
Patterns such as brute force (T1110) followed by time stomping (T1070.006) and credential dumping (T1003.001) can signal an ongoing ransomware campaign, allowing early intervention.
Recommended next steps for SOC and CTI teams
- Integrate Bitsight TI into existing SOC workflows to automate enrichment and threat correlation
- Strengthen collaboration between SOC analysts, CTI teams, and threat hunters
- Continuously monitor the deep and dark web for early signs of targeting or credential leaks
- Use predictive modeling to identify likely adversaries and campaigns before they strike
- Leverage Bitsight’s MITRE-based T-code tracking to monitor, prioritize, and defend against adversary behaviors
Conclusion
SOCs are built for speed, not attribution. Threat intelligence brings the missing context that turns reactive response into proactive defense.
Bitsight’s MITRE ATT&CK-aligned cyber threat intelligence connects internal detections with global adversary behavior, transforming isolated alerts, both the serious and the mundane, into actionable insights. By combining deep and dark web monitoring, behavioral analytics, and T-code mapping, Bitsight enables organizations to predict and prevent attacks before they happen.
With Bitsight TI, SOCs gain the intelligence to connect cyber risk with business impact and stay ahead of emerging threats. Talk to our team to learn more.