Stealer malware is thriving—especially Lumma and Risepro. These logs fuel ransomware, MFA bypass, and persistent access. It's $10 to compromise an account. Explore this and other insights the data reveals.
What Is a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), and Why Should You Care?

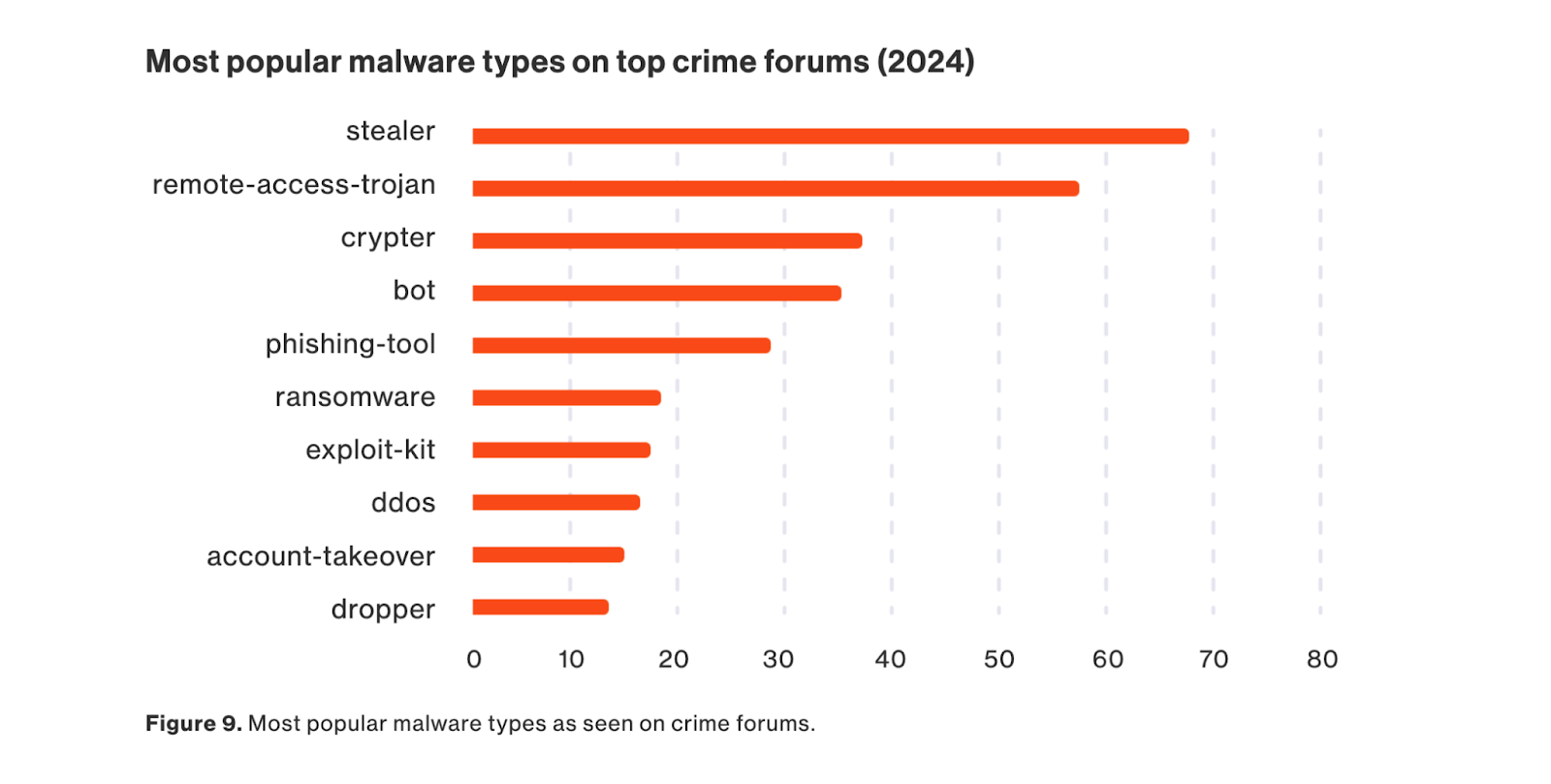
According to our 2025 State of the Underground report—in which we take a look back at cybercrime on the deep and dark web from the past year—384 unique varieties of malware were sold in 2024, an increase from 349 in 2023. To determine this number, our research team examined malware and hacking tools for sale on the top three criminal forums, and as a result, we found that Remote Access Trojans (RATs) were the second most common form of malware in 2024, just behind stealer malware.
The threat is particularly concerning because Remote Access Trojans (RATs) are a form of malware that grants attackers remote control over a victim’s system. Their danger lies in their stealth: they frequently evade detection by masquerading as legitimate programs. They are often leveraged to:
- Steal data (passwords, documents, financial info)
- Monitor activity (keystrokes, webcam/mic)
- Install other malware
- Access privileged files and networks
The growing prevalence of malware—particularly RATs—indicates a significant escalation in the frequency and sophistication of cyber threats. RATs are frequently used by malicious actors to steal information, which can later be sold on the dark web. This stolen data may then be purchased by ransomware and malware operators to further their attacks.
How does a RAT get on my computer?
Remote Access Trojans can infect your system through multiple channels, including compromised websites, malicious file downloads, and deceptive phishing emails designed to trick users into executing the malware. Once in a system, RATs are relatively difficult to detect. Once enabled, some RATs automatically download malware onto the user’s computer.
How do Remote Access Trojans work?
RATs create unauthorized backdoors into devices via network connections, compromising data integrity, system security, and user privacy. NIST defines a backdoor as an undocumented way of gaining access to a computer system. A backdoor is a potential security risk because it allows threat actors to gain unauthorized access to a system.
Once inside a system, a RAT establishes a command-and-control (C&C) channel to create a remote connection, allowing the threat actor to navigate the victim's environment. After infiltration, the RAT enables the attacker to move through the operating system relatively undetected. This access can be used to steal credentials, install additional malicious software, monitor user activity through keylogging, and compromise private files and network resources.
We previously discussed the dangers of stolen credentials, but what's so important about logging keystrokes (aka keylogging)? Keylogging allows threat actors to capture sensitive data such as usernames, passwords, and other confidential information entered on the device. This could enable the threat actor to re-enter the victim's system using the stolen credentials.
Another significant threat is unauthorized access to webcams. While it might not seem alarming at first, let's consider the potential consequences if a threat actor were to gain control of a webcam:
- A major privacy concern is that webcam access enables threat actors to spy on the end user, resulting in a significant violation of privacy and exposing the user to the potential risk of blackmail.
- According to security researchers at IBM, corporate espionage attacks have increased by 25% over the past year. This trend raises concerns about the potential use of RATs in espionage activities.
- The implications of spying extend beyond corporate espionage, malware, and ransomware; it can have profound psychological consequences for the victims.
What about accessing privileged files? Why does that matter?
Remote Access Trojans accessing privileged files is particularly dangerous because it gives attackers the ability to compromise sensitive and critical information, which can have far-reaching consequences. This can lead to:
- Extortion
- Leaking of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) which can result in legal issues
- Security Issues
- Lack of trust in the victim and their security posture
- Creation of more back doors to give the threat actor easier access to the system in the future
How do I protect myself and my organization?
Mitigation strategies
Malware and Ransomware are a persistent threat that should not be taken lightly. Protecting against these risks requires a multi-layered defense strategy focused on prevention, detection, and response.
1. Strengthen credential security
- Use strong, unique passwords for each account—ideally, at least 12–16 characters with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all systems, especially for email, VPNs, and administrative accounts. MFA significantly reduces the risk from leaked or stolen credentials.
- Monitor for leaked credentials: Bitsight offers Cyber Threat Intelligence solutions to help protect you and your company from threats. We proactively scan the deep, dark, and clear web for stolen credentials, collecting 13.2B credentials with 1.23B unique URL-credential pairs in 2024.
2. Use endpoint protection and EDR
- Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools that offer real-time detection and containment of suspicious activity.
3. Maintain secure backups
- Keep regular, encrypted backups of critical data—stored offline or in immutable cloud storage.
- Test backup restoration procedures regularly. Backups must be isolated from your network so they can’t be encrypted by attackers.
4. Train employees and simulate phishing
- Conduct security awareness training to help employees spot phishing emails, social engineering, and suspicious behavior.
- Run phishing simulations to identify weak points in your human firewall.
5. Implement network segmentation and least privilege
- Use network segmentation to limit lateral movement if an attacker gains access.
- Apply least privilege access—users should only have access to the data and systems necessary for their job.
6. Monitor and detect
- Use a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platform to monitor for anomalies.
- Bitsight Cyber Threat intelligence can provide early warning of threats targeting your industry or assets.



