Marsh McLennan Cyber Risk Analytics Center study shows poor performance correlates to higher chance of incident.
What is Vulnerability Management?


The modern challenge
Cybersecurity teams face an unrelenting wave of alerts and newly discovered flaws. With thousands of CVEs disclosed every month, how can you determine which issues actually matter to your organization?
Vulnerability management provides a systematic way to identify, assess, prioritize, and remediate the weaknesses that attackers target most—protecting your business from exploitation and minimizing exposure across your digital ecosystem.
In 2025, this process is increasingly driven by cyber threat intelligence (CTI) and AI-powered automation, enabling organizations to focus on vulnerabilities that truly pose a risk based on real-world exploitation activity, business impact, and threat context.
What is vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management is the continuous process of identifying, prioritizing, reporting on, and remediating security weaknesses across operating systems, browsers, applications, devices, and cloud environments.
A robust IT vulnerability management program helps teams understand their organization’s full attack surface—across both internal systems and third-party environments—and take timely action to reduce risk.
Today’s best programs go beyond scanning and patching. They integrate real-time vulnerability intelligence, such as Bitsight’s Dynamic Vulnerability Exploit (DVE) Score, which predicts how likely a vulnerability is to be exploited in the near term based on active threat actor behavior and dark-web activity.
In short: Modern vulnerability management connects what’s vulnerable with what’s actively being targeted—transforming security operations from reactive to intelligence-driven.
Understanding vulnerabilities
A vulnerability is any weakness in an IT asset that can be exploited by a threat actor to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of data or systems.
Examples include:
- Misconfigured software or network devices
- Insider threats
- Unpatched or outdated software, hardware, or firmware
- Weak authentication credentials or access controls
- Exposed APIs and shadow IT
- Poor encryption or insecure cloud configurations
Vulnerabilities can arise anywhere digital assets exist—on-premises, in the cloud, or across your vendor ecosystem. Attackers often exploit them within hours of public disclosure, making speed and prioritization essential.
How are vulnerabilities classified?
Security teams commonly use the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to assess severity, assigning a base score from 0.0 (None) to 10.0 (Critical). The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) maps these scores to qualitative ratings—Low, Medium, High, or Critical.
However, severity does not equal risk. Many “critical” vulnerabilities never get exploited, while a medium-severity flaw that’s being weaponized in the wild may pose a greater danger. That’s why modern vulnerability management must incorporate real-world threat intelligence—to understand which vulnerabilities are most likely to impact your organization now.
Bitsight’s Vulnerability Intelligence (DVE) goes beyond CVSS to correlate vulnerabilities with active exploitation trends observed across the clear, deep, and dark web, enabling risk-based prioritization at scale.
The vulnerability management lifecycle
The vulnerability management lifecycle is a continuous, five-step process designed to help organizations find and fix weaknesses efficiently.
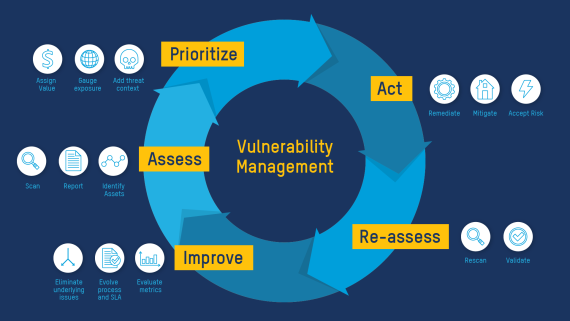
Step 1: Assess
Security analysts begin by building a comprehensive inventory of assets, including endpoints, servers, applications, cloud workloads, third-party systems, and services, as well as their current versions and applied patches. This foundational visibility enables accurate scanning for known and emerging vulnerabilities.
With Bitsight External Attack Surface Management (EASM), organizations gain continuous, outside-in visibility into their digital footprint—including shadow IT, misconfigurations, and unknown assets.
By correlating assets with known CVEs and CTI data, teams establish a dynamic baseline that evolves as new vulnerabilities are discovered. Next comes generating a report to determine which assets are at risk or will need patching or further investigation and remediation.
Step 2: Prioritize
Once vulnerabilities are identified, the next step is determining which to address first. Traditional CVSS scoring provides a starting point, but effective prioritization demands more context.
Security teams should assess:
- Business criticality of the affected asset
- Exposure (external vs. internal)
- Exploit availability and activity in the wild
- Risk level
- Potential impact to operations and data
Bitsight’s DVE Score and Vulnerability Intelligence modules enhance this process by ranking vulnerabilities based on their probability of exploitation, helping teams focus on the 5–10% of flaws that matter most.
This risk-based approach dramatically improves efficiency, ensuring faster remediation of high-risk vulnerabilities while avoiding wasted effort on low-impact issues.
Step 3: Act
Action can take several forms:
- Remediate: Apply vendor patches or upgrades to remove the vulnerability.
- Mitigate: Implement temporary or compensating controls that reduce exploitability.
- Accept: Document and accept residual risk when remediation isn’t feasible or for non-critical assets or systems.
Bitsight AI helps automate this phase by correlating vulnerabilities with remediation guidance, surfacing context-aware recommendations, and tracking patch performance across your organization and vendor ecosystem.
By integrating CTI, you can act faster on vulnerabilities known to be exploited by ransomware groups or discussed on underground markets—before they’re weaponized against you.
Step 4: Reassess
After remediation efforts, teams must verify that vulnerabilities have been resolved. Continuous scanning, penetration testing, and automated validation confirm that fixes were successful and no new weaknesses have emerged.
This stage also generates valuable metrics for leadership reporting, such as:
- Time to remediate (TTR) for critical CVEs
- Number of exploitable vulnerabilities closed per month
- Reduction in attack surface over time
With Bitsight Security Performance Management (SPM), security leaders can visualize remediation progress, benchmark performance, and demonstrate measurable improvement in cyber resilience.
Step 5: Improve
The final—and most important—stage is continuous improvement. Like most cybersecurity workflows, the vulnerability management lifecycle involves continuously evaluating the strategy to verify that the measures in place have successfully reduced or eliminated the prioritized risks. By analyzing metrics and lessons learned, organizations can strengthen their vulnerability management procedures and governance processes.
Regularly revisit scope, tools, and response workflows to ensure your program adapts to evolving threats. Incorporate new CTI feeds, automate repetitive tasks, and integrate external insights (such as vendor exposure data) into your lifecycle.
With Bitsight AI and Cyber Risk Intelligence, teams can now automate detection, contextualization, and prioritization—closing the loop between visibility, action, and governance.
Why vulnerability management must evolve
Vulnerability management is no longer a siloed IT function. It’s a core component of cyber risk intelligence—linking technical security data to business impact.
As digital ecosystems expand across cloud platforms and third-party networks, organizations must continuously monitor exposure both internally and externally. CTI-driven vulnerability management provides that unified, real-time visibility—empowering teams to:
- Anticipate which vulnerabilities are being weaponized
- Prioritize resources based on business impact
- Accelerate remediation timelines
- Communicate cyber risk effectively to executives and boards
Without this intelligence-driven approach, teams risk drowning in alerts and missing the vulnerabilities that actually matter.
IT vulnerability management: Special considerations for complex environments
IT vulnerability management focuses on identifying and mitigating weaknesses across interconnected systems—on-premises, in the cloud, and across hybrid environments.
Unlike traditional infrastructure, modern IT ecosystems include legacy servers, SaaS applications, virtual machines, IoT devices, and unmanaged endpoints. Each introduces unique exposure points and requires different scanning and remediation techniques.
To effectively manage vulnerabilities across such diverse systems:
- Unify visibility by consolidating on-prem, cloud, and third-party assets into one inventory.
- Prioritize by business criticality—a vulnerability on a legacy database supporting financial operations carries higher risk than one on a non-critical web server.
- Integrate scanning tools with external attack surface monitoring to detect misconfigurations and shadow IT.
- Correlate IT asset data with threat intelligence to focus remediation on vulnerabilities that are currently being exploited in your industry.
Bitsight External Attack Surface Management (EASM) extends visibility beyond the internal network to uncover exposed IT assets, monitor them continuously, and correlate findings with active threat data—helping IT and security teams manage vulnerabilities from a unified, external-to-internal perspective.
How Bitsight enhances the vulnerability management lifecycle
As long as there are assets connected to the internet and digital supply chain risk keeps expanding, every organization needs a vulnerability management program. Many industries and regulations require one in order to conduct business and instill trust.
Bitsight enables organizations to take full control of vulnerability exposure with External Attack Surface Management (EASM), Vulnerability Detection, and Vulnerability Intelligence capabilities.
- Continuous external monitoring: Automatically discover and map all internet-facing assets—including shadow IT and third-party infrastructure.
- Actionable vulnerability intelligence: Detect, correlate, and prioritize vulnerabilities based on exploit likelihood using Bitsight’s DVE Score.
- Context-aware remediation: Visualize critical risks, drill into root causes, and track mitigation progress through intuitive dashboards.
- Third-party risk visibility: With Bitsight for Third-Party Risk Management, assess and respond to vulnerabilities affecting your vendor ecosystem during zero-day events.
Learn more about how Bitsight AI and Vulnerability Intelligence can help you predict exploitation, automate prioritization, and manage exp
Vulnerability Management FAQs
What is threat and vulnerability management?
Threat and vulnerability management (TVM) combines the continuous discovery of vulnerabilities with real-time threat intelligence to understand which weaknesses adversaries are actively targeting. By integrating threat context into the vulnerability management lifecycle, organizations can prioritize remediation that meaningfully reduces risk.
What is risk-based vulnerability management?
Risk-based vulnerability management ranks vulnerabilities by exploitability and business impact rather than severity score alone. Solutions like Bitsight Vulnerability Intelligence calculate the probability of exploitation to focus resources on what truly matters.
What does a vulnerability management process look like?
First comes assessing the resources, processes, and tools in place to identify gaps and decide a course of action. Which assets will be monitored for vulnerabilities, and which are the most critical? Who will manage the process, and what tools will they need?
To help answer these questions, Gartner’s Vulnerability Management Guidance Framework lays out five “pre-work” steps aimed at solving the people, process, and technology components:
- Determine Scope of the Program
- Define Roles and Responsibilities
- Select Vulnerability Assessment tools
- Create and Refine Policy and SLAs
- Identify Asset Context Sources
Why is vulnerability management important?
Effective vulnerability management prevents attackers from exploiting known weaknesses—protecting systems, data, and reputation. It’s also vital for compliance, cyber insurance readiness, and executive risk reporting.
What is CVE in vulnerability management?
CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is a standardized identifier for publicly disclosed security flaws. Modern vulnerability management enriches CVE data with real-world intelligence—such as DVE scoring—to determine exploitation likelihood and prioritize remediation.
Ready to reduce risk faster?
Gain real-time visibility into vulnerabilities across your attack surface and supply chain. Learn more about Bitsight Vulnerability Intelligence or request a demo to see how Bitsight AI can help you stay ahead of exploitation.



