Cyber threats don’t start on your network—they start underground. This guide breaks down 7 expert strategies to monitor hacker chatter, track attack tools, and uncover hidden threats before they strike.
How to Prevent Ransomware: Best Practices & Research
The ransomware trend continues to run rampant. One in four breaches involve ransomware, and organized crime actors use ransomware in more than 62 percent of incidents. Cyber criminals are taking advantage of these new opportunities to exploit a greatly expanded attack surface:
- Ransomware attacks doubled in 2021, then spiked again in the first half of 2022
- The overall cost of recovering from a ransomware incident is trending upwards
- In 2021, ransomware attacks on government agencies globally increased by 1,885% over 2020 attacks
- On average, businesses experience 20 days of downtime from ransomware
- One in four consumers will abandon a product or service after a ransomware-related disruption
- From May 2021–June 2022, ransomware groups took credit for 3,640 incidents on their webpages
But ransomware is only one small piece that a security leader has to manage. The threat of ransomware is compounded by a distributed workforce, trends toward technology consolidation, geopolitical upheaval, and budget constraints. Cyber criminals take advantage of vulnerabilities, stolen credentials, phishing, malicious code on web pages, and social engineering to steal a company’s information and sell it back to them.
So what can your organization do to prevent ransomware attacks in a world of constantly evolving and maturing bad actors? Based on industry trends and cybersecurity best practices, here are three steps to prevent ransomware attacks.
3 Steps to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
1) Assess your current state
Many security leaders want to start implementing new defense strategies as soon as they obtain the budget and buy-in they need. The first part of successful ransomware defense is taking a step back and assessing the current state of defense your program is in.
Before spending money on ransomware defense tools and monitoring software, consider the following questions:
- Where do the greatest risks lie in your current network environment?
- How does your cybersecurity hygiene compare to your peers?
- Are you following certain industry or best-practice frameworks when managing your organization’s cybersecurity?
- Do you have visibility into your third parties, and if they have suffered ransomware attacks recently, or historically?
When you have a solid understanding of your current cybersecurity risks, and how you compare to similar organizations and industry frameworks, you can better prioritize ransomware defense efforts to have the highest impact. Utilize frameworks like the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) framework to assess your program against a baseline to determine where to start directing attention.
2) Focus on cybersecurity hygiene
When you have a complete view of your current cybersecurity footprint, the next step to preventing ransomware attacks is to focus on strengthening your program where ransomware threats are most likely to take place.
If you were a ransomware sleuth, you’d probably want access to company payroll information, or employee PII that could be used in a triple extortion attack. Maybe for organizations with high demand goods, like hospitals or oil and gas providers, their most high-stakes operations would be prime targets. Ensuring your network is secure is important even if your organization falls outside the realm of common targets, because ransomware targeting any of your vendor networks can easily make their way into your connected databases.
What are some cybersecurity hygiene practices you can start focusing on? Bitsight data has revealed a proven indication between patching cadence and likelihood of a ransomware attack. By working to patch flagged vulnerabilities quickly, even if larger, underlying remediation strategies haven’t been developed yet, security teams are keeping up with the risk targeting their network.
Of course, overall security hygiene strategies are important in preventing ransomware attacks, including using a vulnerability alert system, routine employee cybersecurity training, endpoint data scanning tools, pre-planned remediation strategies, and more.
3) Don’t be passive
The third best practice for preventing ransomware attacks is to take a proactive risk management strategy, instead of a wait-and-react approach. By the time your security team is actually alerted to an attack, maybe by a publicly announced ransomware breach, or multiple employees reporting phishing emails, there could be more damage done throughout your network, gone unnoticed for weeks, months, or even years.
Don’t wait for ransomware attackers to make themselves known. Utilize a continuous monitoring tool to maintain daily visibility into your network endpoints, and identify changes in your risk portfolio as soon as they even begin to happen. Effective continuous monitoring technology also provides an overall view of network trends so you can identify concerning points that might not stand out if your team were to see them on any one given day.
Bitsight Security Performance Management offering relies on objective continuous monitoring technology to give security teams an outside-in perspective on their network, giving you the view of your network that ransomware attackers can see.
Best Practices for Ransomware Protection
To combat the rise in ransomware attacks, organizations can apply specific strategies to protect themselves against this pernicious threat.
Cyber awareness training and education
Ransomware uses the same attack vectors as other types of malware, including phishing emails, use of compromised credentials, and other means. Employee cybersecurity awareness training can help to protect against ransomware attacks by teaching employees to avoid the poor security practices that make infections possible. For example, training on detecting phishing emails and using strong, unique passwords helps to mitigate some of ransomware’s primary infection vectors.
Establish email security protocols
Ransomware attacks often begin as a seemingly benign link or attachment to an email. Organizations must adopt security awareness programs that train employees on how to avoid ransomware emails and report suspicious email activity. IT security teams need to implement email security protocols such as DKIM, SPF, and DMARC to reduce spoofing and to authenticate the origin of email messages.
Monitor third-party vendors
Even when organizations have top-notch security controls in place, they can easily fall prey to a ransomware attack when security practices of a connected vendor aren’t sufficient. Establishing a process to continuously monitor the security postures of third-party vendors ensures an organization can identify security gaps and recommend remediation strategies effectively.
Continuous data backups
Ransomware’s revenue model is based on selling victims access to their data. It only works if the only way to recover encrypted data is to pay the ransom. By creating regular, read-only data backups, an organization provides itself with an alternative means of recovering lost data. When designing a data backup strategy, it is important to back up regularly to minimize the chance of data loss and to ensure that the backups cannot be encrypted by the ransomware as well.
Avoid peer-to-peer file sharing on networks
Because common ransomware attacks are often prevalent on peer-to-peer file sharing websites, IT teams should monitor and prevent employees from downloading unauthorized files and engaging in file sharing activities.
Increase patching cadence
Poor patching cadence is one of the most concerning risk vectors for organizations. Bitsight’s research has uncovered that patching cadence is a strong overall indicator of security program performance. The more time that passes between availability and implementation, the lower the security performance of the organization. In fact, poor patching performance correlated to a nearly sevenfold increase in ransomware risk for companies with a C grade or lower in Bitsight’s study. To mitigate the risk of poor patching cadence, organizations are encouraged to conduct monthly patches, with the exception of zero-day/out-of-band patches which should be applied ASAP.
User authentication
VPNs, RDP, and other remote access solutions are valuable tools for ransomware operators. A leaked or guessed user password can allow an attacker to remotely access enterprise systems and directly install and execute their malware on corporate systems. Implementing strong user authentication – including the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) – makes it more difficult for ransomware operators to use compromised credentials to spread their malware.
Track security ratings
Monitoring the security ratings of an organization and its vendors can help identify vulnerabilities that hackers may be able to exploit. Bitsight’s research team analyzed hundreds of ransomware events from November 2018 to better understand the relative probability that an organization would experience a ransomware breach. These studies have proven to be a good indicator on for how to avoid ransomware as companies with a low rating are 6.4 times more likely to be a victim than a highly rated company.
Tools for Ransomware Prevention
Cybersecurity visibility into your expanding attack surface is the key to ransomware prevention. After all, you can’t secure what you can’t see. Despite all the latest security solutions, firewalls, and cyber threat intelligence technology, it only takes a single unpatched cloud asset or a vendor with poor security practices to enable a ransomware attack to land within your network.
Ransomware prevention depends on your ability to visualize the common vulnerabilities and exploits in your IT environment and take swift action to address them before they’re discovered by attackers. There are two strategies that can help to accomplish this task: continuous monitoring and security ratings.
Continuous monitoring
In contrast to annual or periodic security audits, continuous monitoring delivers immediate insight into your ecosystem’s risk profile. By continuously assessing and scanning your network for vulnerabilities, security teams can gain immediate insight into your risk profile at any given time. Continuous monitoring offers insight into the entire ecosystem’s security posture, from internal organizations to third- and even fourth-party vendors. This is critical, as more than 90% of companies report experiencing a breach that originated within a vendor’s IT environment.
Security ratings
Security ratings provide an easy-to-understand measurement of an organization’s security performance. By monitoring changes in the security ratings of your organization as well as third-party vendors, you can gain data-driven insights into your greatest areas of risk, allowing your security teams to swiftly remediate them.
For organizations that want to learn how to avoid ransomware, Bitsight enables companies to combines security ratings and continuous monitoring to dramatically improve visibility into security performance.
Anti-ransomware solutions
Ransomware poses a significant threat to companies’ ability to operate and profitability. Protecting against the ransomware threat requires solutions designed specifically to identify, remediate, and restore from ransomware infections. Key capabilities for anti-ransomware solutions include:
- Wide Variant Detection: Many ransomware variants exist, making the ability to detect multiple variants essential for an anti-ransomware solution.
- Fast Detection: Once data encryption has begun, ransomware has already caused damage to the company, so rapid detection is vital.
- Automatic Restoration: Anti-ransomware solutions should automatically restore encrypted data using mechanisms that are not deleted by ransomware (i.e. not shadow copies)
Ransomware Prevention Research
A CISO or cyber risk leader needs the right data to give them insights into where they might be most exposed or at-risk to experience an attack. Over the course of two and a half years, Bitsight’s research team analyzed hundreds of ransomware events to estimate the relative probability that an organization will experience a ransomware event. Four key areas bubbled to the top.
While no organization is immune from determined cyber criminals, there are best practices for minimizing the likelihood of experiencing a successful ransomware attack. Chief among them is a relentless focus on cyber hygiene—a set of essential practices and tasks a company uses to keep systems, data, and users secure every day. Good cyber hygiene significantly lowers the chance of cyber incidents.
Over the course of two and a half years, Bitsight’s research team analyzed hundreds of ransomware events to estimate the relative probability that an organization will experience a ransomware event. The analysis looked back over five six-month periods benchmarked against companies with a high Bitsight Security Rating for security effectiveness. At a high level, the data shows:
- Organizations with a lower Rating increasingly become more likely to become a ransomware target. For example, a Rating lower than 600 is 6.4 times more likely to be successfully targeted by ransomware compared to those with a 750 Rating.
- Poor patching cadence correlates to a nearly sevenfold increase in ransomware risk for companies with a C grade or lower.
- Companies with a C grade or lower in TLS/SSL Configurations are nearly four times more likely to be a ransomware target.
- Companies with a C grade or lower in TLS/SSL Certificates are roughly three times more at risk of a ransomware incident.
Bitsight continuously and non-intrusively assesses organizational cybersecurity performance by evaluating security performance observations across 23 different risk categories. Bitsight processes more than 250 billion security measurements on a daily basis to provide an objective Security Rating based on its observations that is independently verified to be correlated with risk of incident.
Letter grades provide a quick way to understand how a company is performing in each risk type, as well as a meaningful way to compare risk type performance of one company to another. They are directly correlated to how well a company is performing, relative to all companies in the Bitsight inventory:
- Grade A is the top 10% of companies.
- Grade B is the top 30% of companies.
- Grade C is the top 60% of companies.
- Grade D is the bottom 40% of companies.
- Grade F is the bottom 20% of companies.
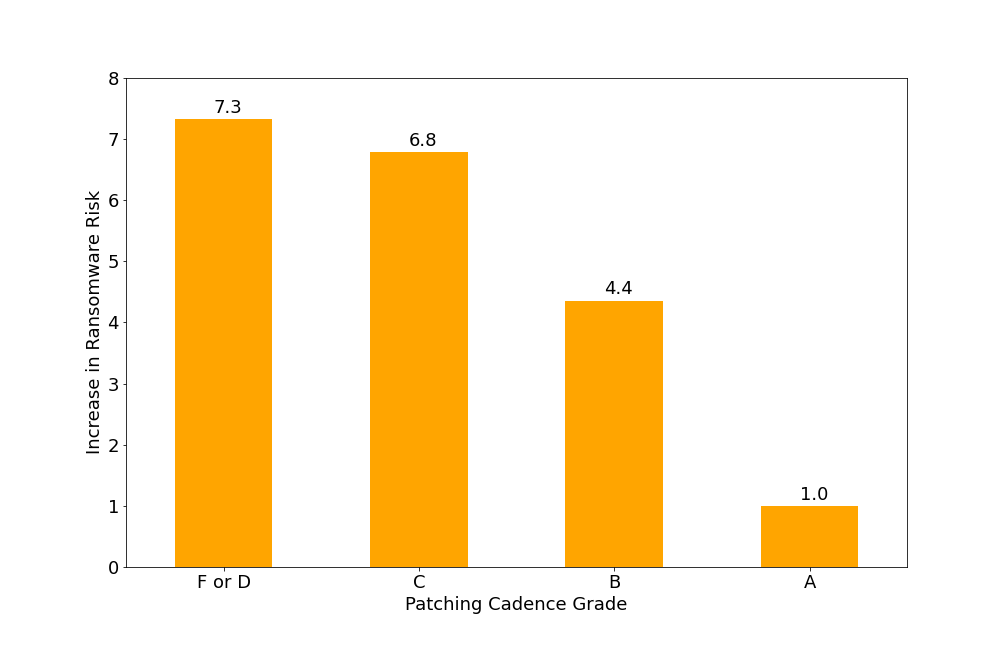
Figure 1: Risk Based on Patching Cadence Grade. Poor patching performance correlates to a nearly sevenfold increase in ransomware risk for companies with a C grade or lower.

Figure 2: Risk Based on TLS/SSL Certificates Grade. Companies with a C grade or lower in TLS/SSL Certificates are roughly three times more at risk of a ransomware incident.
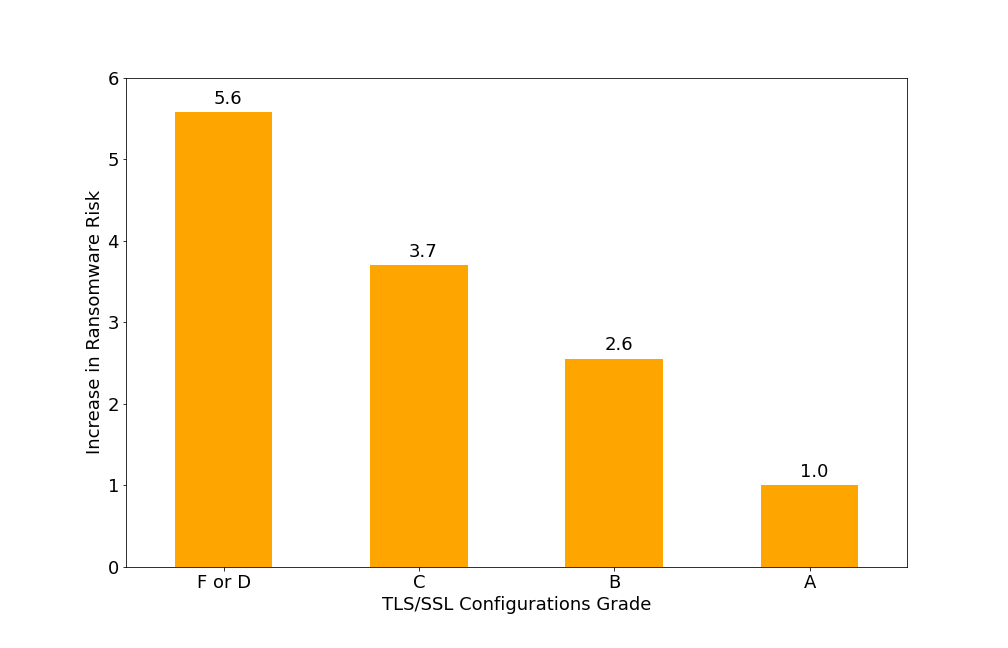
Figure 3: Risk Based on TLS/SSL Configurations Grade. Companies with a C grade or lower in TLS/SSL Configurations are nearly four times more likely to be a ransomware target.
Conclusion: Cyber hygiene matters
It's unlikely that lapsed TLS/SSL encryptions or a missed patch would be the singular, direct cause of a successful ransomware attack. But, it indicates that the cybersecurity program has poor cyber hygiene and may have gaps in vulnerability management, a challenge with Shadow IT, or program management, all of which increases cyber risk. A program with good cyber hygiene and high maturity will effectively address concerns like patch, vulnerability, and configuration management. While the Rating and risk vectors offer specific evidence, the reducing ransomware risk will come from an overall improvement in cyber practices. Risk reduction comes from an overall improvement in practices.
Companies that demonstrate strong cyber health have a lower risk of successful ransomware and other cyber attacks, offering a variety of positive benefits:
- Preventing catastrophic outcomes, such as financial losses and business downtime
- Instilling stronger brand reputation and trust with partners, vendors, and customers
- Increasing the chance of gaining cyber insurance coverage and better premiums
Interested in seeing how effective you are at preventing the risk of ransomware? Get your organization’s Bitsight Security Rating and see how your security compares to industry benchmarks or explore more details about our ransomware research.
Avoiding Ransomware with Bitsight
Bitsight is the world’s most widely adopted security ratings solution, providing data-driven, dynamic measurements of an organization’s security performance. Bitsight enables security performance management and third-party risk management that can help security teams minimize the chances of a successful ransomware attack on their organization.
Security Ratings
All Bitsight solutions are built on Bitsight Security Ratings, which are independently verified to correlate with data breach risk. Rather than conducting periodic scans, Bitsight continuously measures more than 250 billion security measurements on a daily basis to provide an objective security rating based on organization’s performance in 23 risk vectors. These daily cybersecurity ratings range from 250 to 900, with the current achievable range being 300-820. These include in categories like compromised and exposed systems, patching rates, critical vulnerabilities, user behavior, and publicly disclosed data breaches.
Bitsight Security Ratings provide a common language that is understandable by both technical and non-technical employees, executives, and board members. And most importantly for ransomware prevention, independent research shows that Bitsight Security Ratings correlate to data breaches. For example, companies with a Security Rating of 500 or lower are nearly five times more likely to have a breach than those with a rating of 700 or higher.
Security Performance Management
With this Bitsight solution, security and risk leaders can measure the performance of their cybersecurity programs to align investments and actions with the highest measurable impact over time. When determining how to avoid ransomware, Bitsight for Security Performance Management offers insight into the organization’s control of peer-to-peer file sharing, patching cadence, security hygiene, and other security protocols that can help to mitigate the risk of ransomware.
Third-Party Risk Management
This Bitsight solution immediately exposes risk within the supply chain, helping to identify risky issues that could enable a successful ransomware attack originating within a vendor’s network. The insight Bitsight offers into vendors’ security performance enables organizations to act swiftly to help vendors address their security issues and to put controls in place to protect the organization.

FAQs: What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts data and files within an organization’s IT environment or locks users out of their devices. Once the ransomware attack is executed, cyber criminals demand a ransom, usually in the form of bitcoin, before providing the decryption keys that can restore access to the files.
The best strategy for ransomware prevention is to proactively monitor security posture and address vulnerabilities before hackers can take advantage of them. Continuous monitoring and security hygiene are two of the most effective strategies for companies as they seek to understand how to avoid ransomware. Using security ratings, organizations can track their security performance as well as the security posture of vendors to identify vulnerabilities and risks, taking steps to mitigate them before cyber criminals take advantage of them.
Security hygiene is the practice of ensuring that cybersecurity controls, security practices, and security teams are performing effectively every day. Security teams use hygiene to understand the steps needed to maintain the health and security of online systems.


