Ransomware, breach sharing, stealer logs, credentials, and cards. What has shifted and how to respond.
Lumma Stealer Is Out… of Business!
Tags:

Since mid-2024, Bitsight has been collaborating with Microsoft’s Digital Crimes Unit and other partners to dismantle the operational capabilities of Lumma Stealer (LummaC2) — currently the most widely distributed information stealer. Early this week, a coordinated action was carried out to disrupt its operations and take down the supporting malware infrastructure.
Key points:
- LummaC2 is a Malware as a Service infostealer in operation since the end of 2022 that raised popularity among threat actors after a gap in the infostealer scene due to the takedown of Redline and Meta stealers.
- Bitsight TRACE participated in a coordinated action led by Microsoft DCU with private and public partners, to disrupt the malware operation, its command and control infrastructure and the channels where the stolen data is sold.
- LummaC2 infrastructure has been dismantled through the seizure of over 1,000 domains and the shutdown of more than 90 Telegram channels and Steam profiles.
What is LummaC2
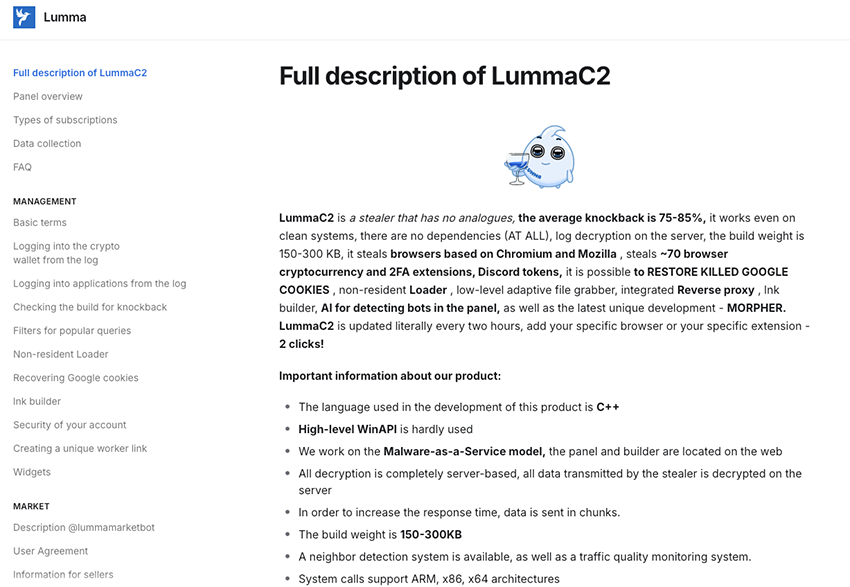
LummaC2 is the successor of LummaC, an infostealer operating under the Malware as a Service (MaaS) model. Advertised on various underground forums since late 2022, the malware has undergone significant development with frequent updates and new versions since then. The actor, known by aliases including Shamel, LummaStealer, and LummaC2, promotes the malware's features and updates through underground forums and a Telegram channel.
The malware targets Windows systems (from Windows 7 x32 to Windows 11 x64) to extract sensitive data. Its main function is data theft from various applications, including browsers, password managers, VPNs, FTP clients, cloud services, remote desktop, email clients, cryptocurrency wallets. It can also be configured to extract any other type of data from infected machines.
The operators of LummaC2 maintain a Telegram bot to sell the stolen information collected by their affiliates.
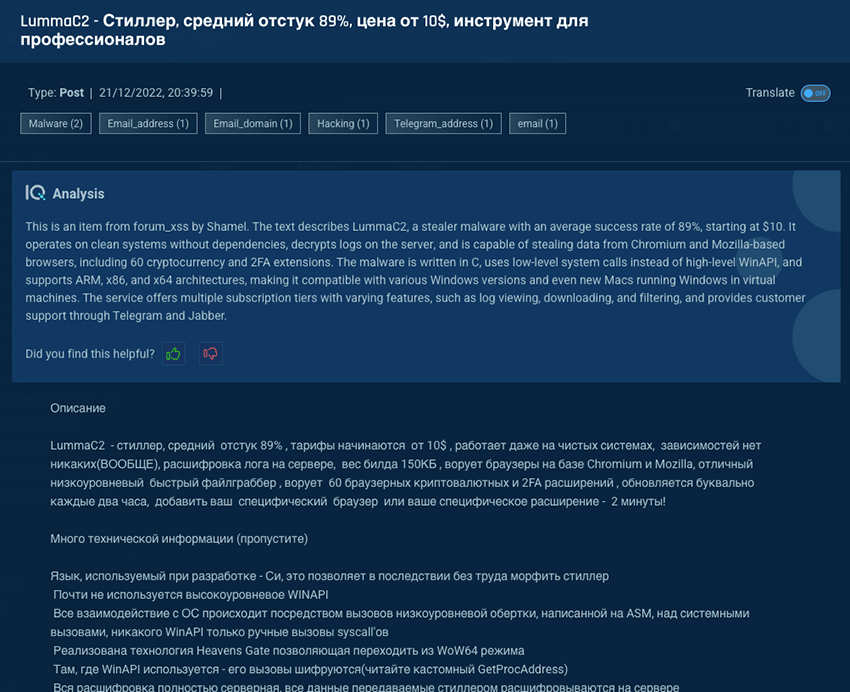
The actor also maintains the documentation of the malware in a public website, which proved to be one of the best pieces of malware documentation available to date. Lumma malware has become a popular choice for threat actors due to its capabilities, frequent updates, user-friendliness, active support and price - it is available through subscription packages ranging from $250 to $1000 USD. A full package that includes the source code is available for $20000 USD.
It became more popular following the October 2024 takedown of Redline and Meta stealers in Operation Magnus, which created a gap for threat actors that want to employ stealer capabilities on their criminal activity.
LummaC2 Infrastructure
Over time, the command and control (C2) infrastructure of the malware became more complex, especially in its later versions, mirroring the evolution of its features and the effects of a security industry proactively taking down C2 domains as they were pushed to the wild.
The more recent version of LummaC2 employed a multi-tiered command and control (C2) infrastructure. Its characteristics included:
- A tier-1 of frequently changing domains, hardcoded within the malware's configuration. Normally nine domains.
- A secondary, fallback mechanism activated if communication with the primary domains failed. This involved a hardcoded domain often concealed within Steam profile URLs. The profile name served as the domain and was obfuscated using a ROT cipher with varying rotations (11-15).
- In recent builds, the malware may include a Telegram channel URL, where the channel name is also the domain obfuscated with a ROT cipher.
- If present, the concealed domain in the Telegram channel becomes the primary C2 server the malware attempts to connect to. Secondly tries the primary list of domains and, if those fail, tries to use the concealed domain in the Steam profile.
- The majority of these domains were behind Cloudflare proxies in order to hide the true C2 and maintain resilience between domain updates.
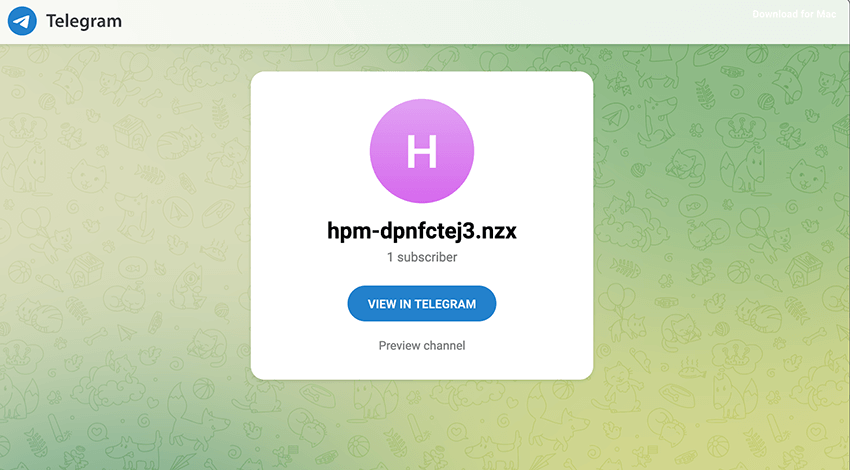
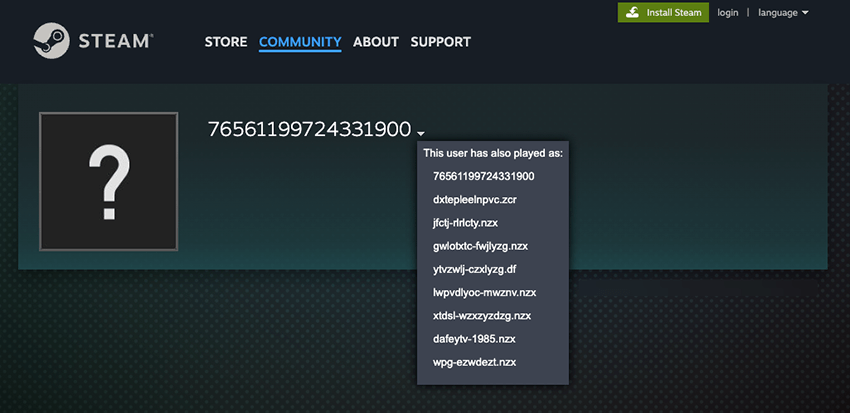
Investigation of LummaC2 infrastructure revealed over 1000 tier-1 command and control domains, 63 primary domains, and 93 Telegram channels used for domain distribution. Additionally, 17 fallback domains utilizing 4 Steam profiles were identified. These infrastructure elements were seized during this action.
One is None, Two is One.

We expect this action to shake up the threat landscape a bit. Threat actors will probably adjust to get back to business and stay competitive in the malware scene, or their piece of the market will be taken over by others in a crowded space. Bitsight will remain vigilant, continuing to monitor the threat actor’s activity and watching for any signs of retooling or resurgence.
Disruptive actions such this effectively combat criminal activity and send a strong message, creating operational chaos and disabling trust among threat actors. These actions are most impactful when public and private partners collaborate, forming task forces with diverse skills and perspectives.
Bitsight TRACE thanks Microsoft DCU, ESET, Lumen’s Black Lotus, CleanDNS, Cloudflare and Europol for their efforts and cooperation.
To learn more about Lumma Stealer capabilities read the MSTIC blog here.
To learn more about infostealers you can check Bitsight’s prior work here and here.
Indicators of Compromise
A compiled list of indicators of compromise (IOCs) including C2 IP addresses and domains gathered over the past two years. This information is provided to aid researchers and network defenders in identifying and eliminating LummaC2 infections within their networks.
IOCs are available in your preferred format at the following links:
Happy hunting. Over and out.



